March_Automotive MCU|Automotive MCU Market and Technology Analysis(Next)
vehicularMCUTechnical Trend Analysis
With the trend of electrification and intelligentization, automobile functions are becoming more and more complex, resulting in the increasing use of electronic control units, which in turn leads to a huge increase in the amount of data and makes it impossible for traditional communication methods to meet the demand for real-time transmission and processing. Therefore, a few car manufacturers take the lead in integrating and centralizing automotive functions by replacing electronic control units with a few domain control units (DCUs), then reducing the number of DCUs through cross-domain convergence, and finally being replaced by zone control units (ZCUs) to form a centralized centralized control framework, Bosch has divided the development blueprint of automotive electronics and electrical architecture into six phases: modularization, integration, domain centralization, cross-domain integration, vehicle integration, and vehicle cloud computing.
- Modularization, where each electronic control unit is responsible for a single function, is the architecture used in most cars today.
- Integration is the process of reducing the number of functions performed by a powerful electronic control unit to reduce costs.
- Domain centralization is the integration of all electronic control units into five functional domains: power, chassis, body, intelligent cabin, and autonomous driving. Each dedicated domain control unit is connected via Ethernet and CANFD (Control Area Network with Flexible Data Rate). The power, chassis, and body domains only involve control instruction calculation and communication, and require less computing power, so 32-bit MCUs can be used, as listed in Table 2.
Table 2, Five Functional Domains Control Unit Features
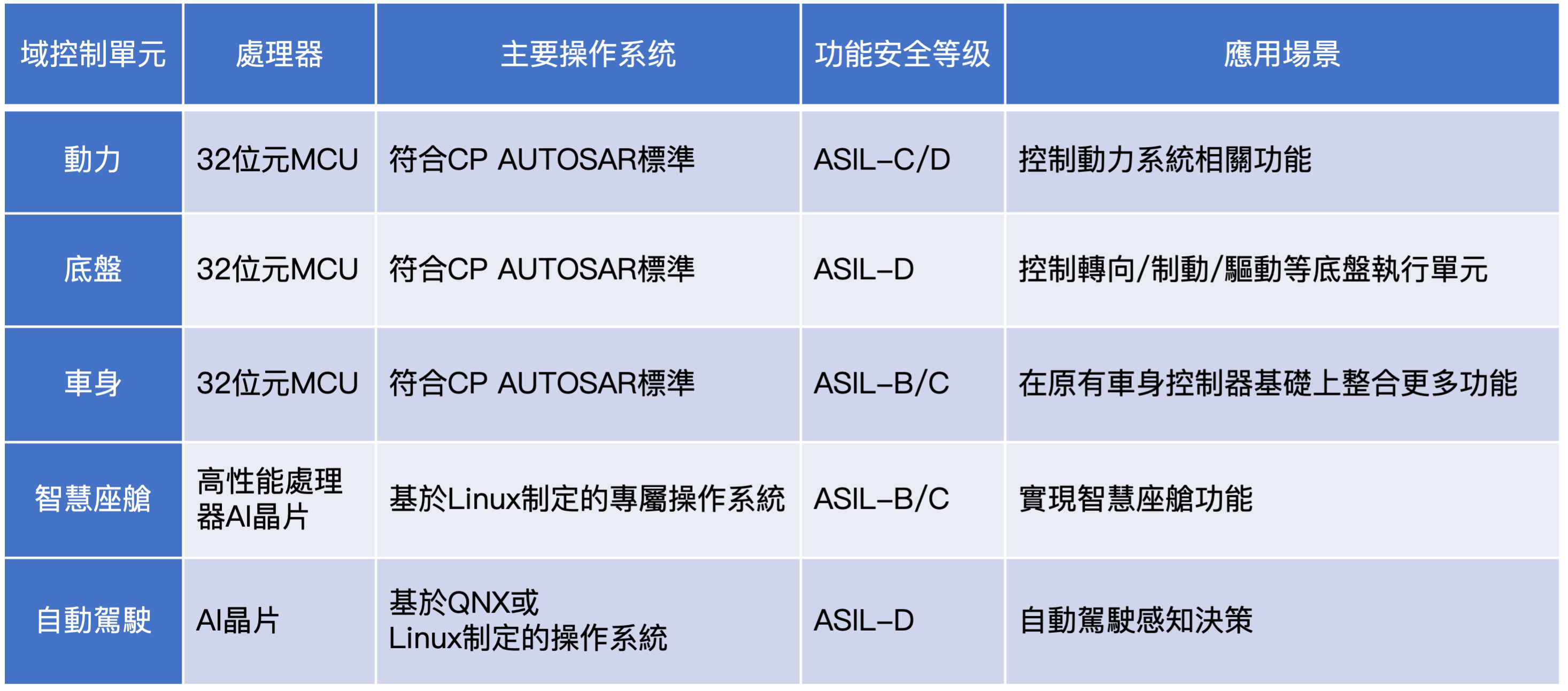
Source : Gaijin Automotive Research Institute