March_Bioenergy Analysis|What is Bioenergy and International Market Trend
While green energy has been attracting attention from all walks of life in recent years, the biomass energy industry, which has been developed in Taiwan for a long time, is still quietly contributing to the clean energy field, even though it does not appear on the news like offshore wind power and solar energy, which are the focus of attention. "Biomass energy is energy derived from the recycling and reuse of biomass metabolites, including plants, trees, animals, and microorganisms, which are converted into biofuels through combustion, fermentation, and gasification. This conversion process not only reduces the use of agriculture, forestry and organic waste, but also reduces the reliance on fossil fuels. In addition, compared to renewable energy sources such as wind and solar energy, biomass energy has a unique advantage. Wind and solar power generation is intermittent, and its stability is affected by weather, day and night, and seasonal variations, whereas biomass energy can be converted into chemical energy (e.g., biomass diesel or biomass ethanol) through physical or chemical means for storage, and then taken out to be used when it is time to generate electricity. Therefore, biomass energy is more flexible to environmental change than renewable energy sources such as wind power and solar power. However, from the perspective of net-zero carbon emission, not all biomass energy belongs to the category of renewable energy. According to the definition of the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC), traditional biomass energy treatments, such as direct charcoal combustion or animal feces, are excluded from the category of renewable energy due to the lack of "treatment" to reduce carbon emissions. According to Taiwan's Renewable Energy Administration Regulations, the definition of biomass energy equipment is that the fuel source used for power generation equipment should be 100% agriculture, forestry, plants, biogas, or treated organic waste, so it can be seen that the difference between biomass energy and biomass energy lies in the source of the fuel and whether or not the fuel source has been "treated", therefore, in order to understand what biomass energy is, we need to discuss in detail the issue from raw materials to treatment and application. Therefore, in order to understand what biomass energy is, we need to discuss it from its raw materials to its treatment and application.
Biomass feedstocks, products, and related applications
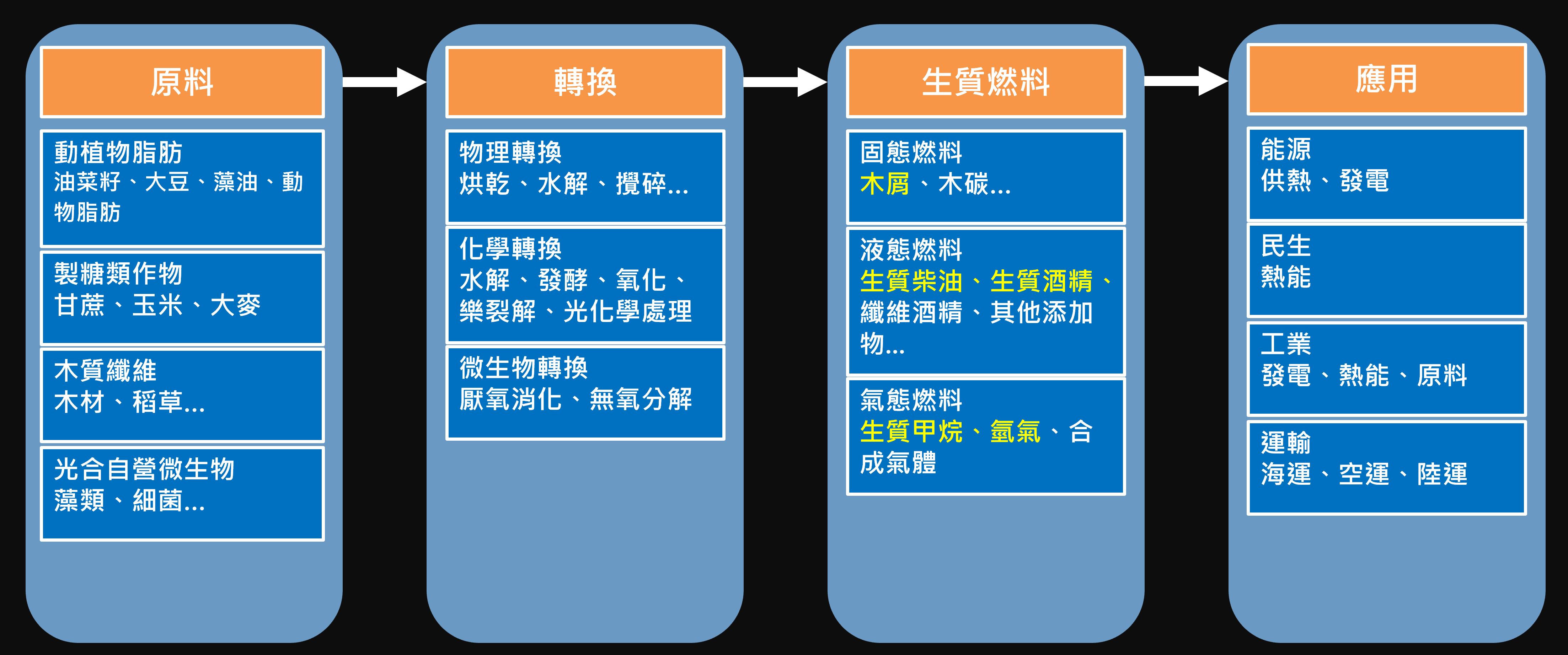
Biomass energy from raw material to application is divided into four main stages: "raw material", "conversion", "biomass fuel" and "application" as shown in Fig. 1.
Figure 1 Biomass Energy
Source:Ji Pu Industrial Trend Research Institute 2023/06
1. "Raw Material": The raw material sources of biomass energy are extremely diversified, including organic waste from agriculture, forestry and industry, and even animal manure, plants, trees, etc. These raw materials are collected and processed into animal and vegetable fats, such as rapeseed, soybean, algal oils, and animal fats, which can be used to produce biodiesel, which are rich in fats and can be transformed into combustible energy through the conversion technology. These substances are rich in fat, which can be converted into combustible energy through conversion technology. This is currently the most widely used source of biomass energy in industry and power generation (the product is biodiesel). Secondly, sugar crops such as sugar cane, corn and barley are rich in carbohydrates, which can be converted into biomass methanol or other combustible energy through fermentation. The third is wood fiber, which is processed through gasification and cracking to convert cellulose-rich wastes such as wood and straw into combustible gases or other forms. Finally, there are photosynthetically active microorganisms such as algae and bacteria, which can convert light energy into chemical energy through photosynthesis and store it in their organisms for conversion into biogas, methane, etc., which can be used to generate electricity or other forms of energy.
2. The "conversion" stage is the process of turning biomass raw materials into usable energy. These conversion processes include combustion, fermentation, gasification, etc. Depending on the nature of the conversion, they can be divided into three main types: physical conversion, chemical conversion, and biological conversion. Physical conversion is the most basic conversion process, which mainly includes drying, hydrolysis and crushing. In this process, the physical structure of the biomass is altered for subsequent processing; for example, the biomass can be dried to remove excess water, pulverized to increase its surface area, or hydrolyzed to release its chemical components. Chemical conversion is a more complex conversion process than physical conversion, in which other compounds and catalysts are used to change the chemical structure of the biomass to produce biomass materials, including hydrolysis, fermentation, oxidation, cracking, and photochemical treatment, etc., to produce combustible gases, liquids, or solid energy. For example, biomass can produce ethanol through fermentation or heat through oxidation. The third type is microbial conversion, which is a conversion process utilizing microbial activity, mainly including anaerobic digestion and anaerobic decomposition; in this process, biomass is decomposed by microorganisms to produce combustible gases such as methane, e.g., biomass can be put into an anaerobic digestion reactor, and after a period of time, anaerobic digestion will produce combustible methane gas.
3. After the conversion process of "biofuel" is completed, the biofuel produced includes solid, liquid or gaseous fuel, as shown in Figure 2.
Figure 2 Three types of bioenergy

Source: Newjust
Solid Fuel: This type of fuel mainly includes wood chips, wood carbon, etc., which is the earliest form of biomass fuel utilized by human beings. solid fuel has the advantages of convenient storage and low transportation cost, but it may produce a large amount of solid waste and gas emissions during the process of use. the global solid biomass fuel market was US$221.7 billion in 2022, and is expected to reach US$425.8 billion by 2027 at a CAGR of 9.81 TP3T. The global solid biofuels market is expected to grow at a CAGR of 9.8% to reach 425.8 billion in 2027. Europe is the largest production region accounting for about 34%, in which Sweden and Finland and other Nordic countries, due to the extensive forest area, wood waste will be converted into solid biomass fuels used in the field of power generation and heating. North America (Canada and the U.S.) is also a major producer of solid biofuels for the same reason, accounting for about 30%.
Liquid fuels: These fuels consist mainly of biodiesel, bioethanol, cellulosic alcohols and other additives. The main advantage of liquid fuels is their high energy density and their ability to be used directly in existing internal combustion engines and diesel generators, but their manufacturing process may consume large amounts of water and energy. The global liquid biomass energy production market is US$81 billion, and is expected to grow at an average annual rate of 6.5% to reach US$126.5 billion in 2030, of which North America (mainly the U.S.), due to the development of agriculture, soybeans, wheat, corn, and other sources of biomass fuels, coupled with the early development of biomass energy policy, so it has become a major producer of liquid biomass energy production of biomass ethanol and biodiesel, accounting for about 40%. Brazil is the second largest producer of biofuels in the world, mainly producing bioethanol from sugarcane, which is suitable for tropical areas. European liquid biofuels account for about 20% of the world's liquid biofuels, and the main production country is Germany, which utilizes rapeseed oil as the raw material for refining bio-diesel. In the Asian region, Indonesia and Malaysia are the two Southeast Asian countries that are the global leaders in palm oil production, so the use of palm oil production waste to be processed into biodiesel is the main output of these two countries.
Gaseous fuels: These fuels mainly include biogenic methane, biogenic biogas, synthetic gas, etc. These fuels are usually produced through microbial fermentation or gasification processes. These fuels are usually produced through microbial fermentation or gasification processes, and have higher energy conversion efficiency and environmental friendliness (compared with coal, methane and other biogas have lower greenhouse gas emissions), but storage and transportation are also more difficult, and require suitable facilities and equipment. It is expected to grow at a CAGR of 7.2% to reach US$187.3 billion in 2030. Asia is the main region of the ecological biomass energy market accounting for more than 35%, with China as the leader and the largest biogas fuel country (including biomass methane and other gases), followed by India, these two countries have a large amount of agricultural and animal husbandry waste, and are actively developing the use of agricultural and biological excreta resources for the production of biogas, as China's 14th Five-Year Plan has stipulated that by 2030, biomass power generation will reach US$107.7 billion. As China's 14th Five-Year Plan has stipulated that the application of biomass energy for power generation should reach 8% of the total power generation capacity by 2030, it is estimated that China will continue to maintain the leading position in terms of the market share of gaseous energy. In the Americas, the U.S. is the main country with active investment and policy support for biogas production, including biomass methane, while Brazil in South America is also utilizing waste from the livestock industry to refine biogas.
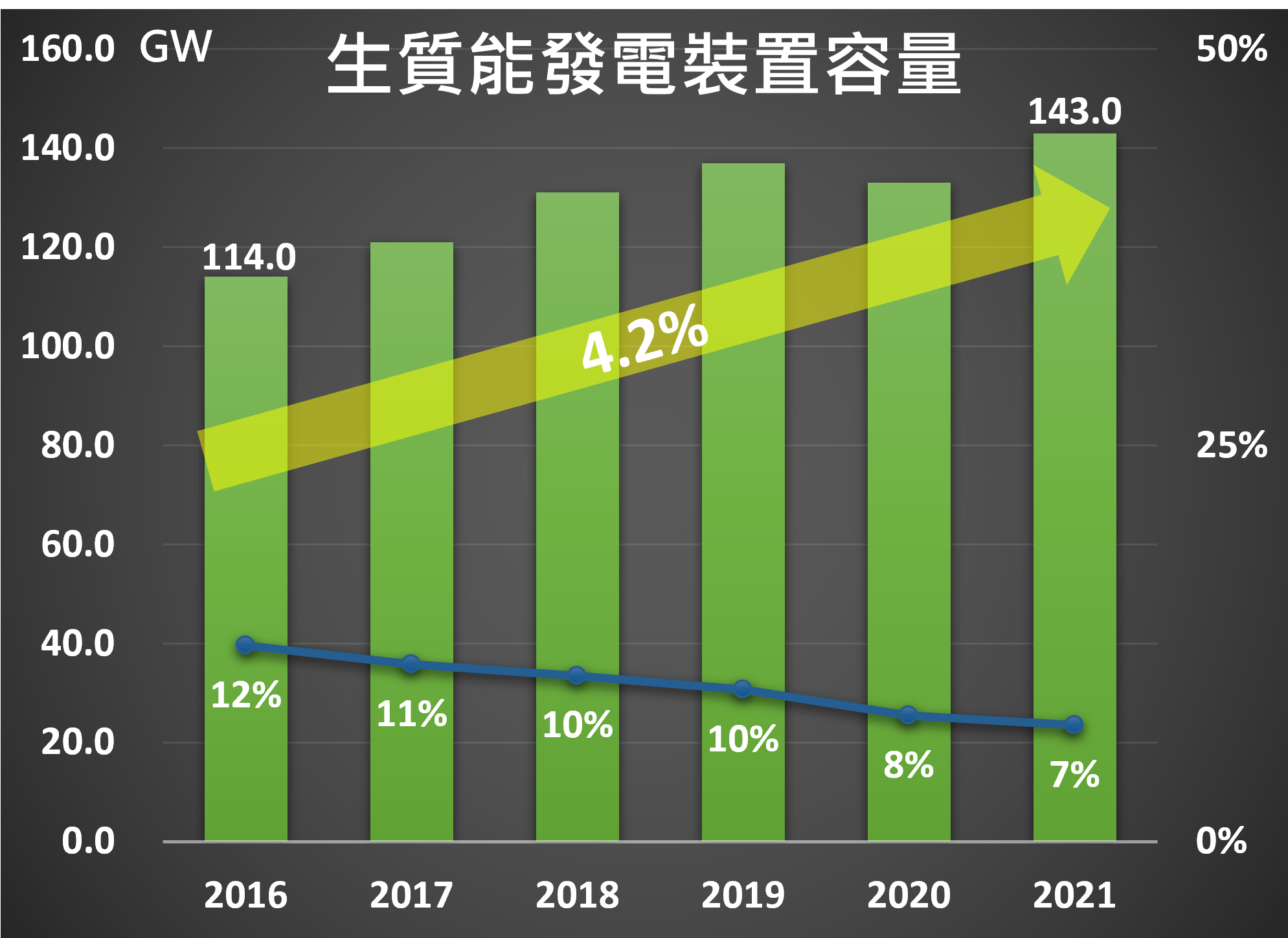
4. 『Application』: Biomass fuels are used in a wide range of applications, including electricity, heat and transportation fuels. These fuels can be used for residential, commercial and industrial heating and power, or as fuel for cars and airplanes. In the power generation sector, the world's biomass power market was impacted by the outbreak of the epidemic in 2020, with total installed capacity shrinking by about 3% to 133GW for the year, but with the easing of the epidemic and the promotion of policies in various countries, biomass installed capacity has rebounded to 143GW in 2021, however, despite the recovery of biomass installed capacity, it has been slow to grow compared with other renewable energy sources. However, despite the recovery of biomass energy installation capacity, growth has been slow compared to other renewable energy sources. Since 2016, biomass energy has grown at an average annual rate of only 4.2%, much slower than the growth rate of green energy sources such as wind (14%) and solar (25%). This has caused the share of biomass energy in the renewable energy market to gradually shrink to 7% in 2021, as shown in Figure 3. Nevertheless, it is estimated that by 2030, the market value of the entire biomass energy industry will reach US$210 billion at a compound annual growth rate of 5.7%. If we look at the regional development of biomass energy generation in 2021, the total annual biomass energy generation will be about 660TWh, with the highest share of 43% (284TWh) in Asia, where China's biomass energy generation is the highest in a single country at 146TWh and is planned to reach 8% of the overall power generation capacity in 2030; and the second largest share in Europe is about 33%.
Figure 3 Biomass Power Generation Capacity
Source:Ji Pu Industrial Trend Research Institute 2023/06