February_Carbon Trading|From Carbon Pricing Mechanism to Carbon Trading: China's Carbon Trading Current Situation (Next)
China has officially become the world's largest carbon emitter since 2005, and by 2021 its carbon emissions will be 1,081 TP3T higher than those of the U.S., reaching 11.9 billion tons. In order to achieve China's carbon neutrality goal by 2060, it is planned to peak carbon emissions by 2030 and introduce a carbon quota mechanism and utilize the carbon trading market to encourage corporate participation. The current status of carbon trading in China is the same as that of foreign countries in terms of the carbon trading market and carbon emission control, with the main trading targets being "Carbon Allowance" and "Certified Carbon Emissions Reductions (CCER)", and the actual emissions of the controlled enterprises being composed of Initial Allowance + Trading Allowance (for over-expansion of emissions) + CCER (for over-expansion of emissions). The actual emissions of the controlled enterprises are composed of initial quota + trading quota (only for over-emission) + CCER (only for over-emission).
Figure 1: China's Carbon Neutral Target and Trading System
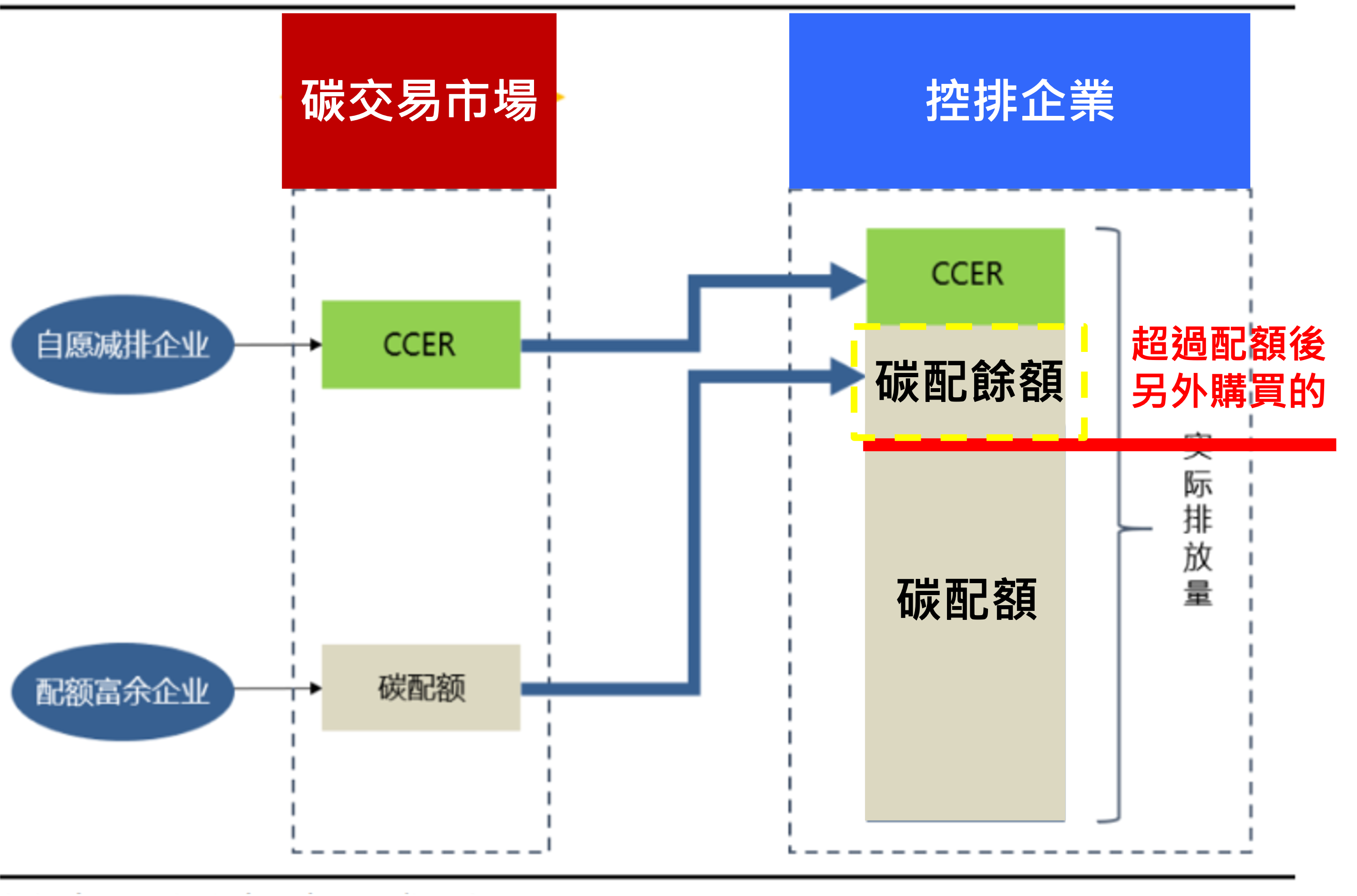
source : China Development and Reform Commission