Industry Trend Report|Impacting the Future of the Technology Industry Compound Semiconductors Play an Indispensable Role
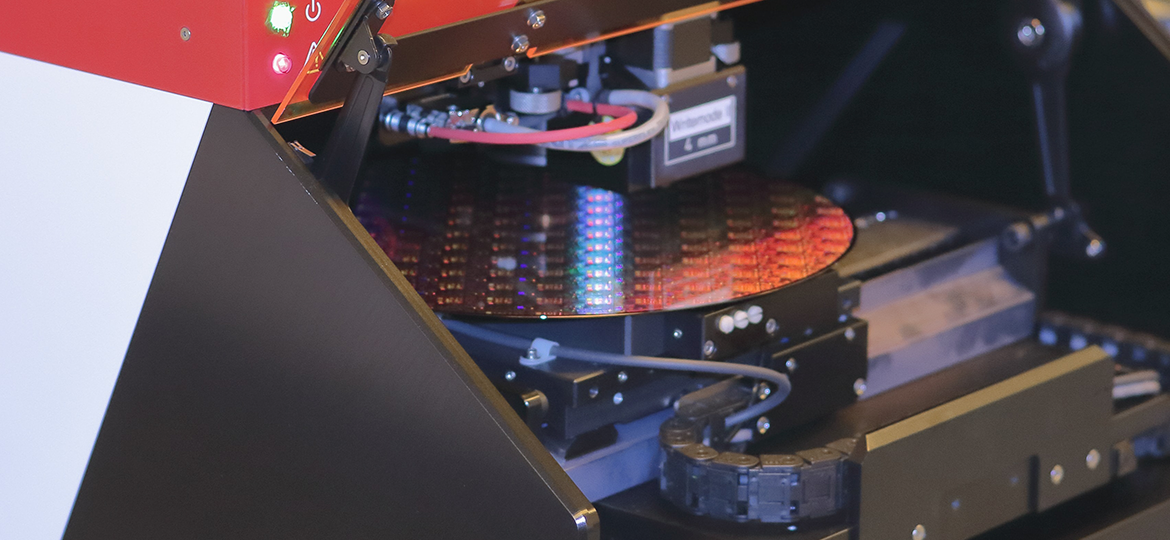
Compound semiconductors are semiconductor materials composed of atoms of two or more elements, mainly from the III-V, II-VI, and IV-IV groups of the Periodic Table. Common binary compound semiconductors include GaAs, GaP, InP, and GaN from III-V, CdSe, CdTe, and ZnSe from IV-IV, SiC and SiSe from IV-IV, and SiC and SiMe from IV-IV. ), Cadmium Telluride (CdTe) and Zinc Selenide (ZnSe) in Groups II-VI, Silicon Carbide (SiC) and Silicon Geode (SiGe) in Groups IV-IV, and Aluminum Gallium Arsenide (AlGaAs), Aluminum Inductance Arsenide (AlInAs), Aluminum Nitride (AlGaN), Aluminum Phosphorus Gallium Phosphide (AlGaP), Indium Nitride (InGaN), Cadmium Zinc Telluride (CdZnTe) and Zinc Nitride (CdZnTe) in Groups II-VI, and in Groups II-VI, Silicon Carbide (SiC), Phosphorus Input (InP) and GaN, Cadmium ZnTe and CdZnTe. CdZnTe) and mercury cadmium telluride (HgCdTe). Gallium arsenide and phosphor are generally categorized as second-generation semiconductors, while third-generation semiconductors are gallium nitride and silicon carbide. Comparisons of the various semiconductor materials are shown in Table 1, with an emphasis on the third-generation semiconductors, which are the ones that have attracted a lot of attention in the market and are experiencing the best growth.