April_Hydrogen Energy Analysis|Low Carbon Hydrogen Energy Industry Development and Trends(Up)
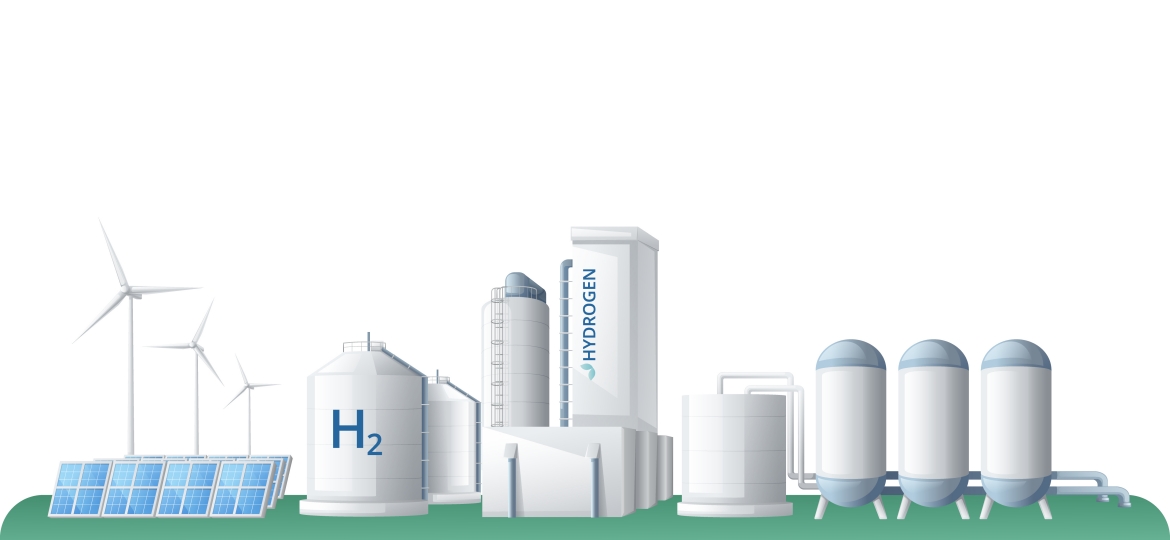
Hydrogen is the first element on the periodic table and one of the most abundant elements in the universe. Since hydrogen does not contain carbon atoms, its combustion only produces water and does not emit carbon dioxide (Figure 1), and it is regarded as one of the renewable energy sources. Due to its abundance of resources, high energy density, and wide range of applications, hydrogen has been recognized by the IEA as one of the key components of the net-zero carbon emission scenario for the year 2050. Currently, there are three main ways to use hydrogen for power generation, including nuclear fusion, thermal power generation and fuel cell power generation; among them, nuclear fusion has not yet been successfully commercialized due to the high technical difficulties; while thermal power generation and fuel cell power generation have become two mainstream ways of hydrogen power generation due to the maturity of the technology.